Course Description
This course explores how increasing globalisation, rapid technological change and pressures on sustainability have all opened expansive international opportunities, while also fuelling significant threats for today's small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The course highlights the role of international markets for the sustainability of small and medium-sized organisations that build their competitive edge on creative problem-solving. While this is key to growth and winning against the competition, it is resource-intensive and therefore often only profitable once it reaches critical mass internationally. Students explore how, in today's highly dynamic and interconnected world, enterprises are well served to use the principles of effectuation to take an iterative path forward, using resources at hand as contingencies are identified. Students will assess affordable losses and potential gains, and learn how to co-create with diverse stakeholders to achieve a wide-reaching impact. Further attention is paid to how the internationalisation process affects enterprise operations in terms of intellectual property, risk management, governance, and financing.
Learning Outcomes
- Describe the economic importance and the need for SME internationalisation in today’s globalised environment.
- Identify and analyse the micro-foundation of SME internationalisation including attitudes, mindsets and cognitive approaches associated with exploring international opportunities.
- Evaluate the social, political, economic, cultural and ethical challenges of the internationalisation process, and design appropriate responses to overcome these challenges.
- Devise strategies for SMEs to acquire knowledge, partnerships, and networks for creating value internationally.
Learning Experience
Topics
- The Role of SMEs and the Entrepreneur in a Globalised World
- SME Internationalisation: Opportunities and Challenges
- The Internationalisation Process
- Cognition and Mindsets
- International Strategies for SMEs
- Funding and Support for the Global Firm
- International Performance of SMEs
- Immigration and Global Entrepreneurship
- Internationalising a Family SME
- Social Entrepreneurship and Impact Investments
- Digital Entrepreneurship
Development Team

Chanaka Wijewardena
Course Author
Lead

Kat Alchin
Learning Designer
Lead

Alexis Milligan
Digital Education Developer
Lead
Assessments
-
Graded Discussions
Discussion
Learners respond to a series of discussion board posts, expressing their view on the topics throughout the course. They also engage in discussion by responding to the ideas and perspectives of their peers.
10%
-
Entrepreneurship Case Study Analysis
Case Study
Learners produce a brief report that analyses the internationalisation process and needs of two Australian firms, through the lens of entrepreneurship.
20%
-
Group Presentation
Media Task
Working in a group, learners conduct an in-depth analysis of the small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) sector in a specific country in the Asia-Pacific region and propose strategies to enhance its international competitiveness.
5%
-
Change Implementation Executive Report
Report
Utilising a case study of a SME getting ready to start internationalising, learners analyse the case through the lens of theories, models and concepts discussed during seminars, and recommend growth strategies for the business.
35%
Snapshots
Learning Resources
-
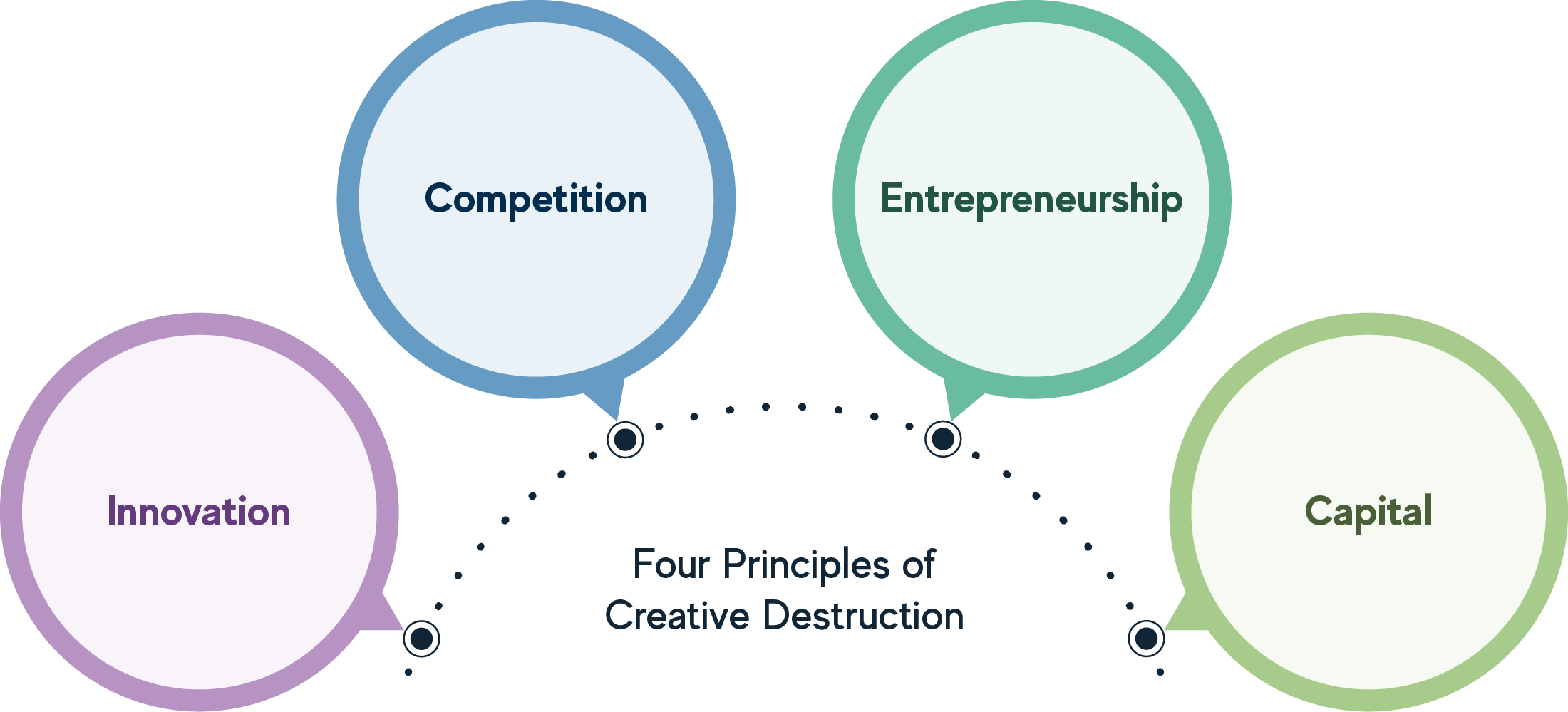
Schumpeter's view of creative destruction
Visualisation of Schumpeter's 4 pillars of creative destruction: innovation, competition, entrepreneurship and capital.
-
Personal characteristics that can prevent you reaching your goals and objectives
Entrepreneurs may need to work on attitudes and habits that prevent them from reaching their goals and objectives. This activity will help you understand some of these personal characteristics and why it is important to avoid them.
-
Motivations to Internationalise
In this video, you're introduced to two SMEs: Goolwa Pipi Co. and Woods Bagot. Each guest gives a brief introduction to their firms, before discussing some of the motivations for each of the firms to move into new markets.

